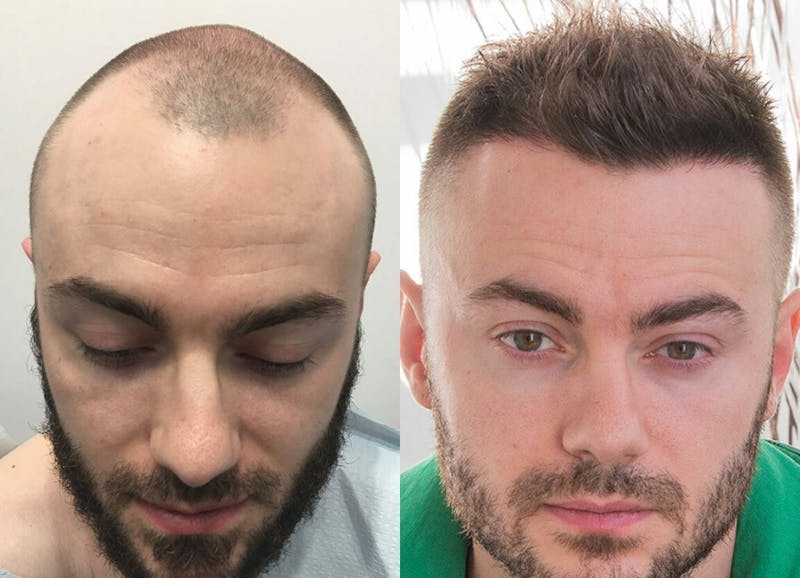
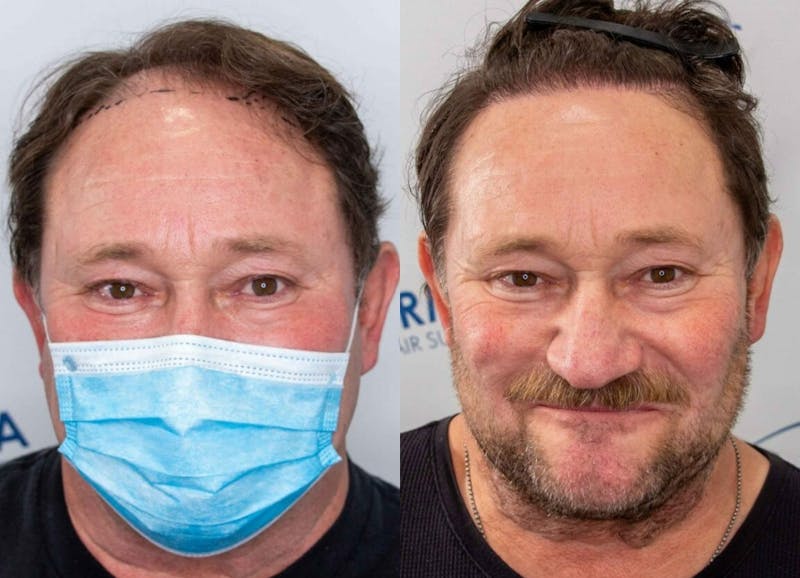
Hair Transplant in Toronto, Ontario
At the Canadian Plastic Surgery Centre in Toronto, we provide advanced hair restoration solutions tailored to your needs. Our state-of-the-art facility and expert hair transplant surgeons and techs specialize in modern techniques like FUE (Follicular Unit Extraction) and NeoGraft®, ensuring natural, seamless, and long-lasting results. Schedule a complimentary consultation today to learn more about your options.
Schedule a complimentary consultation today!
Schedule
Dr. Anil Sharma
Dr. Anil Sharma is a distinguished physician specializing in cosmetic procedures and hair restoration surgery. Born and raised in England, he graduated from the University of Glasgow Medical School, one of the UK's oldest and most prestigious institutions. After completing higher surgical training at the Northwestern Deanery, he practiced general medicine in London and worked at Transform, one of Europe's largest private cosmetic surgery clinics. He later co-owned the London Medical Group, a private clinic in central London. Dr. Sharma has trained in Milan, Paris, and London, mastering the latest techniques in cosmetic medicine and skin surgery.
What is FUE (Follicular Unit Extraction)?
FUE is a minimally invasive hair transplant method where individual hair follicles are harvested from the donor area (typically the back of the scalp) and transplanted into areas of thinning or balding. This cutting-edge technique avoids the need for a linear incision, making it an excellent choice for those seeking a discreet and effective solution.
Why Choose FUE?
- No linear scarring – perfect for short hairstyles
- Faster recovery and minimal downtime
- Precision placement for natural-looking results
- Ideal for small to moderate areas of hair loss
Our skilled surgeons ensure that every graft is carefully placed to match your natural hairline and density, creating results that are virtually undetectable.


How about FUT (Follicular Unit Transplantation)?
While FUT (Follicular Unit Transplantation) is available, we often recommend FUE for its superior recovery, lack of visible scarring, and modern approach. FUT may be an option for certain cases involving extensive hair loss, but our focus remains on minimally invasive, patient-friendly solutions like FUE.
NeoGraft: The Advanced FUE Solution
The NeoGraft® system is an automated FUE technology that enhances precision and efficiency. By automating the follicle extraction process, NeoGraft delivers superior graft quality while minimizing discomfort and downtime.
NeoGraft benefits include:
- Automated precision for consistent, high-quality results
- Reduced trauma to the scalp for healthier grafts
- Faster procedure times and quicker recovery
- Natural hairlines that restore confidence
NeoGraft takes FUE to the next level, making it a preferred choice for patients seeking modern hair restoration.

Why Choose the Canadian Plastic Surgery Centre for Hair Restoration?
- Expert Surgeons: Specialists in minimally invasive hair restoration techniques.
- Cutting-Edge Technology: Featuring NeoGraft® for advanced FUE procedures.
- Natural Results: Customized hairlines that blend seamlessly with your existing hair.
- Comprehensive Care: From consultation to follow-up, your satisfaction is our priority.
Ready to take the first step toward a fuller, natural-looking head of hair? Schedule your consultation with the Canadian Plastic Surgery Centre today. Let us help you rediscover your confidence with FUE and NeoGraft.